In the proceeding five centuries, humanity has made incredible progress in discovering and understanding natural laws. Starting in the sixteenth century, the Early Modern Period, colloquially known as the Scientific Revolution, catapulted humanity into the modern era. Today our knowledge of nature's inexorable laws extends from the largest possible structures in the Universe to the smallest physical components that construct all of reality.
However, a study of the history of science makes it clear that we did not build up this knowledge from either the top down, or the bottom up. We started in the middle. Presumably, humanity discovered the "simplest" laws first (i.e. we picked the low hanging fruit), but this assumption begs the following question:
If nature's various laws at different scales are built up and atop of the laws at lower scales, why and how is it that nature conspired to the laws found at our human scale the easiest to understand?
A Strange Nadir of Complexity
Quantum Field Theory (QFT) predicts the behavior of nature's most fundamental components. Notoriously, the subject is incredibly complex. General Relativity, the modern theory of gravity, goes the other direction. It predicts the behavior of matter at the largest scales. And it too is famously difficult to understand and work with. Both are inventions of the advanced mathematics of the twentieth century and both require nearly a decade of dedicated work to understand and manipulate.
Yet, we can and do teach Newton's Laws to high schoolers.
Mathematics doesn't work this way. Students start with elementary counting and arithmetic, then study geometry, algebra, and a host of other topics in roughly the same order that we discovered them. Physics too is taught in a historical manner, but there—because of the unique phenomenon we're discussing—students must be later told to disregard their previous knowledge when learning new subjects. Mathematics, by contrast, will never instruct students to disregard earlier truths when moving on to more complex ones.1 Arithmetic is not invalid when learning calculus, in fact the opposite is true. Yet, an intuitive understanding of Newtonian Mechanics is useless and even harmful when discussing General Relativity.
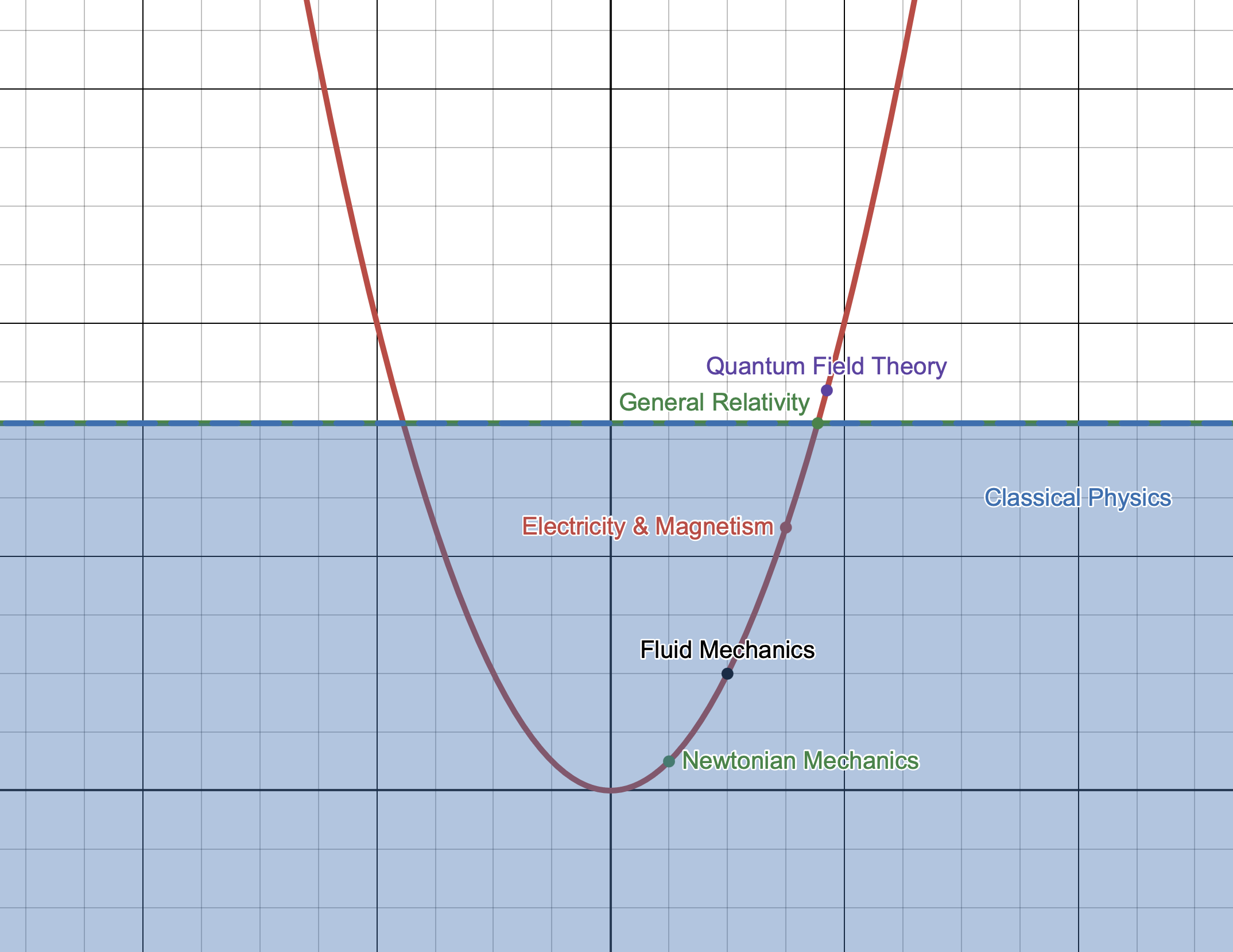
It's almost as if natural laws have this inherent complexity curve that bends upward toward the ends. If so, then that idea would tend to suggest that we function at the perfect place, where physical laws are at their most powerful (complex enough to allow for complex and emergent phenomena like life) while also being at some nadir in computable complexity.
But why should this be so?
An Anthropic Viewpoint
Perhaps, though I see no direct evidence to support this argument, it is the case that the laws of nature simply appear less complex at our familiar human scale because we are the ones formulating the laws. Thus the rules by which we construct these laws are somehow intuitively complementary to our human intuitions about the workings of the Universe at that same scale.
Newton's Laws are convenient for describing earthly motion and humans evolved on earth, hence our mathematics bakes in some of our innate intuition about how the world works.
This explains how, when phenomena are more distant from our day-to-day experience, their physical and mathematical descriptions become increasingly complex and non-sensical.
However, this anthropic approach sheds no light on precisely what sorts of intuitive principles we've baked into our mathematics and, looking at the commonly-used ZFC axioms which underly much of modern mathematics, it's hard to see exactly what "human intuitions" can be found there, at least from my perspective.
Wondering Aloud
For now, it remains something of a mystery to me exactly why this phenomenon of the strange dip in complexity exists. I'm sure that I'm not the first to see or wonder about this curious case, but I'm also not sure precisely how to search for or investigate this topic further. If anyone knows more or can recommend a few papers or a book on the subject, please get in touch.
